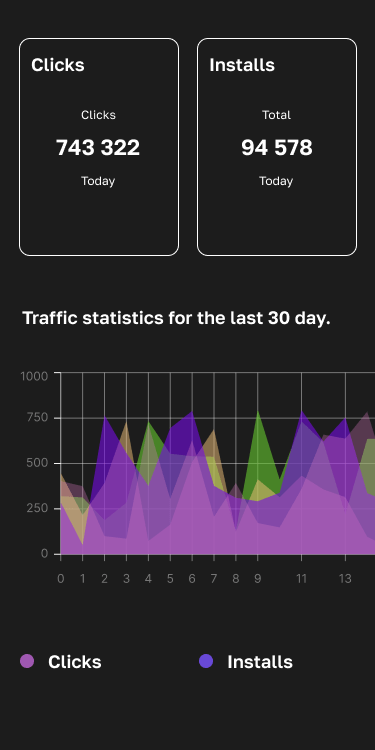
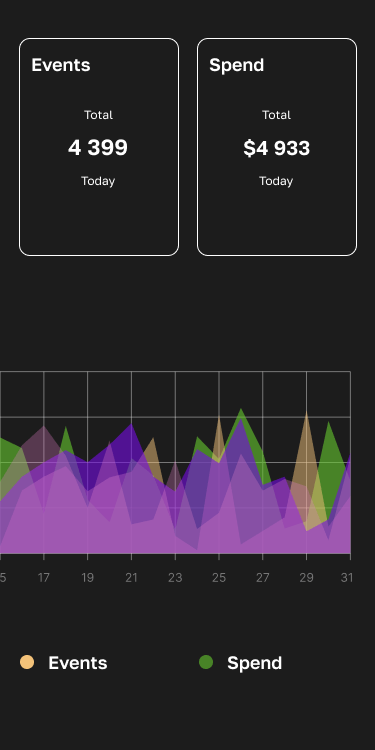
At scale, mobile user acquisition stops being about channels and starts being about mechanics. OEM traffic and in-app advertising are often discussed side by side, but treating them as interchangeable is one of the fastest ways to lose efficiency. Both channels can drive growth, but they behave very differently under pressure. Understanding where each one works — and where it breaks — is critical for UA managers and advertisers building sustainable performance models.
1. Why CPI and Scale Are No Longer Enough
| Legacy UA Logic | Why It No Longer Works |
| Lowest CPI wins | CPI no longer correlates with user value |
| Scale first, optimize later | Optimization windows are shorter and noisier |
| Install equals success | Post-install behavior defines real performance |
| Attribution is precise | Privacy changes reduce signal quality |
The modern UA question is no longer how many installs a channel delivers, but how reliably it delivers users who retain, convert, and monetize.
2. Two Channels, Two Types of Demand
Demand Mechanics Comparison
| Dimension | In-App Traffic | OEM Traffic |
| User state | Active inside another app | Exploring device or system |
| Nature of demand | Interruptive | Contextual and latent |
| Discovery moment | Mid-activity | Device setup or system navigation |
| Intent formation | After the click | Before the install |
| Role in funnel | Demand discovery | Demand capture |
3. Core Strengths and Limitations
Channel Capabilities
| Aspect | In-App Traffic | OEM Traffic |
| Speed of scale | High | Moderate |
| Creative flexibility | Very high | Limited but contextual |
| Cost model | Auction-driven | Inventory-defined |
| Cost volatility | High | Low to medium |
| Early retention | Inconsistent | More stable |
| Attribution clarity | High but noisy | Often undervalued |
4. Hidden Economics UA Teams Often Miss
Cost Behavior at Scale
| Factor | In-App | OEM |
| Budget elasticity | High | Limited |
| CPI behavior | Increases with scale | More stable |
| Impact of competition | Strong | Moderate |
| Predictability | Lower | Higher |
Intent Filtering Stage
| Channel | When Intent Is Filtered | Practical Implication |
| In-App | After install via events and LTV models | Requires strong post-install optimization |
| OEM | Before install via placement context | Cleaner early cohorts |
LTV Distribution Shape
| Metric | In-App Traffic | OEM Traffic |
| LTV curve | Wide, long-tail | Narrow and concentrated |
| Outliers | Many | Few |
| Median predictability | Low | High |
| Payback modeling | More complex | Easier and more stable |
5. Where Scaling Breaks: In-App Traffic Mistakes
Common In-App Scaling Errors
| Mistake | Result | Corrective Action |
| Scaling low CPI sources | Retention collapses | Gate scale by early events |
| Scaling single creatives | Creative fatigue | Scale creative clusters |
| Ignoring auction dynamics | CPI inflation | Gradual budget ramps |
| CTR-driven decisions | Low-intent users | Optimize beyond installs |
6. Where Scaling Breaks: OEM Traffic Mistakes
Common OEM Scaling Errors
| Mistake | Result | Corrective Action |
| Treating OEM like in-app | Quality degradation | Scale by scenario, not spend |
| Cutting too early | Missed value | Extend evaluation windows |
| Over-optimization | Performance instability | Optimize in large iterations |
| Last-click bias | Underinvestment | Measure incrementality |
7. Attribution Reality Check
| Attribution Aspect | In-App | OEM |
| Last-click credit | Usually captured | Often lost |
| Organic overlap | Lower | Higher |
| Assisted installs | Less common | Common |
| Incrementality visibility | Medium | High when measured correctly |
8. How Experienced UA Teams Combine Both Channels
Strategic Role Allocation
| Strategic Role | OEM Traffic | In-App Traffic |
| Establishing quality baseline | Yes | No |
| Driving performance upside | No | Yes |
| Market entry | Yes | Conditional |
| Rapid experimentation | No | Yes |
| CAC stabilization | Yes | No |
| Aggressive scaling | Conditional | Yes |
Final Takeaway
| Key Insight | Why It Matters |
| Channels are not interchangeable | Each breaks differently at scale |
| CPI is not performance | Intent and LTV define value |
| OEM is stable, not slow | Stability improves predictability |
| In-app is powerful, not risky | Discipline determines outcome |
OEM and in-app traffic are different layers of the same acquisition stack.
UA teams that win long-term are not those chasing the lowest CPI, but those who understand where demand forms, how intent is filtered, and where performance breaks at scale.
That is what turns traffic into sustainable growth.